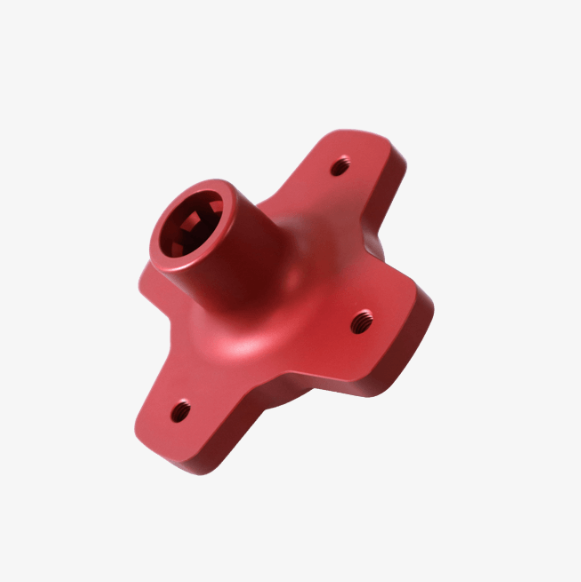
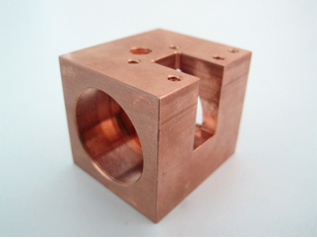
Precision CNC Milling Services
China high-quality precision CNC milling services you can trust. Competitive pricing and fast lead times.
Over 60 Certified Materials
±0.005mm Tight Tolerance
Custom Finishes
Lead times from 7 days
Customer data security
Our Maximum capabilities for CNC Milling
Experience unparalleled accuracy and quality in your prototyping and production runs with our cutting-edge 3 and 5-axis milling centers.
Attain the highest performance standards while crafting intricate parts that fulfill even the most stringent requirements.

3-axis and 3+2-axis CNC Milling
3-axis and 3+2 axis CNC milling machines provide an economical solution for producing parts with simpler geometries. These systems offer a low cost of entry as compared to other machining processes, making them ideal choices where affordability is critical.
| Size | Metric Units | Imperoal units |
| Max. part size for soft metals & plastics | 2000 x 1500 x 200 mm 1500 x 800 x 500 mm | 78.7 x 59.0 x 7.8 in 59.0 x 31.4 x 27.5 in |
| Max. part for hard metals | 1200 x 800 x 500 mm | 47.2 x 31.4 x 19.6 in |
| Min. feature size | Ø 0.50 mm | Ø 0.019 in |
5-axis CNC milling
5-axis CNC milling centers have the capability to deliver superior quality parts while markedly increasing efficiency. With fewer setups required, they offer a cost-effective solution for achieving complex geometries quickly and accurately.
| Size | Metric Units | Imperoal units |
| Max. part size for all materials | 650 x 650 x 300 mm | 25.5 x 25.5 x 11.8 in |
| Min. feature size | Ø 0.50 mm | Ø 0.019 in |
CNC Milling General Tolearances
We provides a variety of CNC machining tolerances tailored to your specific design needs, including GD&T callouts. Depending on your part’s geometry and selected
material, we accommodate standard and custom thread sizes, achieving tolerances up to ±0.001″. Our default CNC milling tolerances for metals follow ISO 2768-m,
while for plastics, we adhere to ISO 2768-c.
Materials For CNC Machining Parts
wEoffers a wide variety of materials for custom CNC machining, plastic, and metal, including but not limited to:
CNC metal
| Materil | Photo | Alloys: | Finishing Options: |
| Aluminum |  | 6061-T6, 7075-T6, 2024, 5052, 6060, 5083, 2017, 6082 | Alodine, Anodizing Types II, III, III + PTFE, ENP, Media Blasting, Nickel Plating, Powder Coating, Tumble Polishing |
| Stainless Steel |  | SS303, Stainless Steel 304/304L, Stainless Steel 316/316L, Stainless Steel 17-4, Stainless Steel 416, etc. | As machined, Bead Blasted, Polishing, Decorative Chrome Plating, Powder Coat, Nickel Plating, Gold Plating, Silver Plating |
| Alloy Steel |  | AISI 1215, AISI 4140, AISI 4340, AISI 8620, AISI 4130 | Polishing, Plating, Painting, Powder Coating and etc. |
| Tool Steel |  | A2 Tool Steel, D2 Tool Steel, O1 Tool Steel, S7 Tool Steel, M2 Tool Steel | Bead/Sand Blast, Polishing, Plating, Painting, Powder Coating, Heat Treatment and etc. |
| Brass |  | C360, C260 | Nickel Plating, Bead Blasted, Gold Plating, Silver Plating |
| Copper |  | C10100, C11000, C12200, C14500, C17200 | Plating, Polishing |
| Titanium |  | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo, Ti-3Al-2.5V | Polishing, Anodizing, Sandblasting, Chemical etching, Laser engraving and etc |
CNC Plastics
| Material | Photo | Color | Grade |
| POM (Delrin/Acetal) |  | White, black, brown | POM-C, POM-H, UV stabilized POM, Food-Grade POM |
| PMMA (Acrylic) |  | Transparency | Extruded PMMA, Cast PMMA, Impact-Modified PMMA, UV-Stabilized PMMA, Heat-Resistant PMMA |
| PEEK |  | Beige with no transparency | Unfilled PEEK, 30% glass-fiber reinforced PEEK, 30% carbon-fiber-reinforced PEEK, Bearing Grade PEEK |
| ABS |  | ABS is naturally opaque and comes in a range of colors including black, white, and gray | General purpose ABS, Flame retardant ABS, High impact ABS, Heat-resistant ABS |
| Nylon (PA) |  | Nylon is often used in its natural off-white or slightly yellowish color | Nylon 6, Nylon 6/6, Nylon 11, Nylon 12 |
| PTFE (Teflon) |  | The color of PTFE is typically white or off-white | |
| PVC |  | clear or opaque | UPVC, PPVC, CPVC |
| PEI (Ultem) |  | Amber or brownish color | Unfilled PEI, Glass-Filled PEI, Carbon-Filled PEI, Ultem PEI |
Surface Finishes for CNC Machined Parts
We offers a wide selection of surface finishes to improve the surface qualities of CNC-turned parts.
The surface finishes applied after machining can change the appearance, surface roughness, hardness, and chemical resistance of the produced parts.
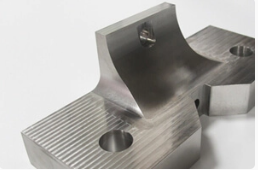
As machined (Ra 3.2μm / Ra 126μin)
This finishing option with the shortest turnaround time. Parts have visible tool marks and potentially sharp edges and burrs, which can be removed upon request

Smooth machining (Ra 1.6μm / Ra 63μin)
Smooth machining is similar to a ‘As machined’ finish, but with less visible machine marks. Parts are machined at a lower feed rate, with no hand polishing.

Polishing (Ra 0.8μm / Ra 32μin or better)
Polishing is the process of creating a smooth and shiny surface by rubbing it or by applying a chemical treatment.

Bead Blasting
Machined parts are bead blasted with glass beads which results in a uniform grainy texture and reduced machining marks.

Tumbled
It is a process that tumbles vibrating media on machined parts to remove sharp edges and burrs.
Tumbling can be used to remove machine marks from exterior surfaces
.

Bead blasted + Anodizing type II
The parts are bead blasted to #120 grit before being anodized type II—ideal for increasing the aluminum part’s corrosion resistance and cosmetic effects.
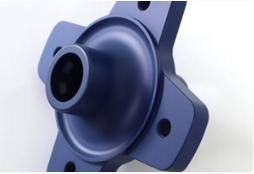
Bead blasted + Anodized type III (Hardcoat)
The parts are bead blasted to #120 grit before being anodized type III. Type III (Hard Coat) is thicker and adds a wear-resistant layer to Type II’s corrosion resistance, suitable for functional applications.

Black Oxide
Black oxide is a conversion coating that is used on steels to improve corrosion resistance and minimize light reflection.

Powder Coated
This is a finish of applying powdered paint to the components and then baking it in an oven, which results in a stronger, more wear- and corrosion-resistant layer that is more durable than traditional painting methods.

Chromate Conversion Coating
Chromate conversion coating is used to improve the corrosion resistance of aluminum and aluminum alloys while keeping their conductive properties. It is also applied as a base layer prior to priming and painting parts

Plating
Include Nickel Plating, Silver Plating, Gold Plating, Zinc Plating, Chrome Plating, Tin Plating and etc, it is ideal to reduce corrosion, improve the appearance and function of solderability and electrical conductivity.

DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) Coating
DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) coating is a hard, wear-resistant coating made of a carbon-rich material that exhibits some of the properties of diamonds
Other surface finishes are also available. Learn more about our metal and plastic surface finishing capabilities here.
Overview: What is CNC Milling?
The Basics Of CNC Mills
CNC milling is a computer-controlled manufacturing process that uses a rotating cutting tool to remove material from a workpiece to create a desired part or product. CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control, meaning a computer program precisely controls the milling machine’s movements and operations. The workpiece is securely held in place in CNC milling while the cutting tool moves along multiple axes to shape the material according to the digital design. This process can create complex geometries, intricate details, and high-precision parts.
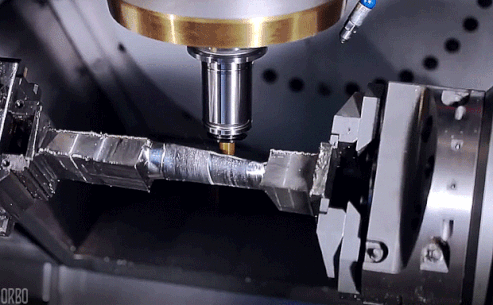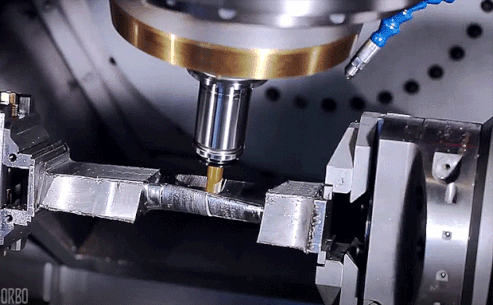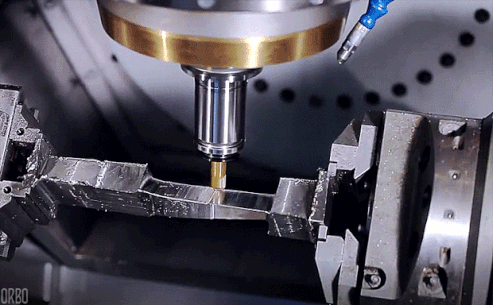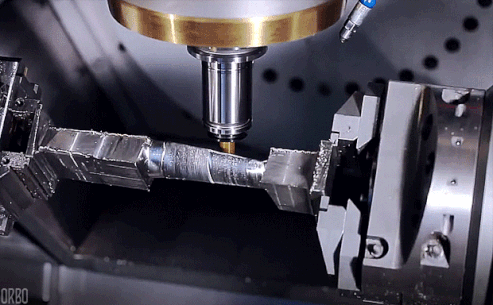
How CNC Milling Works
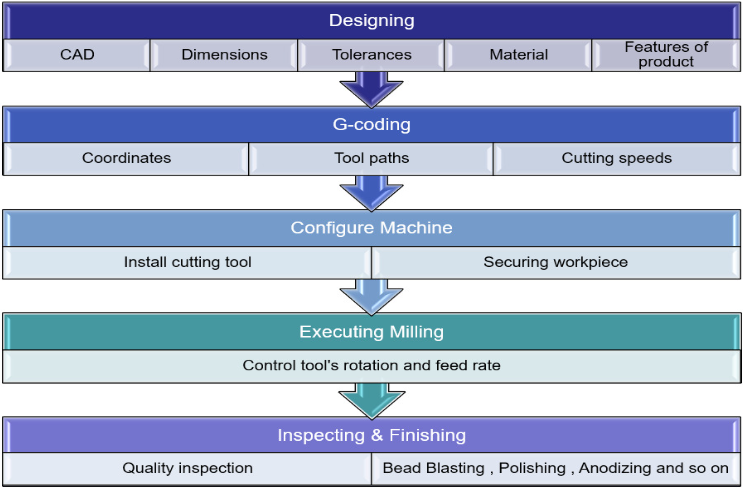
Designing: Engineers or designers use computer-aided design (CAD) software to generate a digital 3D model containing dimensions, tolerances, and features of the final product.
• G-coding: The CAD file is converted to machine-readable G-code instructions, providing coordinates, tool paths, and cutting speeds for the CNC milling machine.
• Configure Machine: The CNC machine is prepared with the appropriate cutting tool, secured workpiece, and configure settings according to G-code instructions.
• Execute Milling: The CNC machine follows G-code commands, moving the cutting tool along multiple axes to remove material from the workpiece at controlled rotation and feed rates, achieving the desired shape and dimensions.
• Inspection and Finishing: After milling, the part is inspected for accuracy and quality. Additional processes like deburring, polishing, or surface treatments may be applied to meet final product specification
Quality assurance
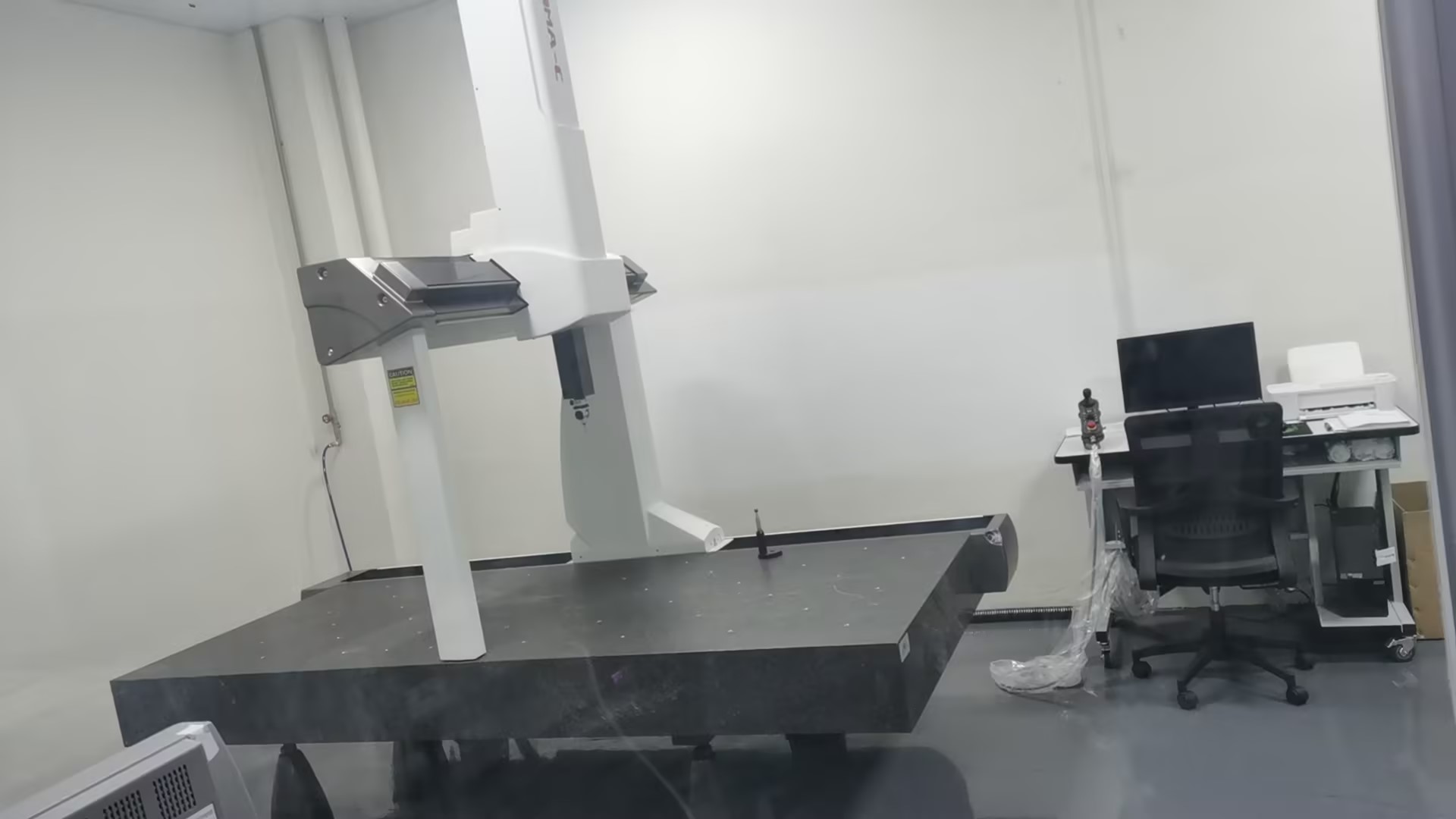

Material Inspection: We carefully verify the materials used for your project, ensuring they meet the desired quality standards and match your specific requirements.
Skilled Workforce: Our experienced and highly skilled machinists and engineers closely monitor every step of the machining process, ensuring each part meets the desired tolerances and specifications.
In-Process Inspection: Throughout the manufacturing process, our quality control team conducts regular inspections and measurements to detect and address any deviations or errors promptly.
Final Inspection: Once the parts are machined and finished, our quality control team performs a thorough final inspection, checking dimensions, surface finish, and other required specifications. This guarantees that each part meets your expectations before shipping.
CNC Milling FAQs
5-axis CNC machining is a method used to create complex parts using a computer-controlled machine. Imagine it as an advanced robotic sculptor that can move its carving tool in five different directions to shape a piece of material. In simpler terms, the machine’s cutting tool can move along three basic directions—up and down, left and right, and forward and backward. These movements are referred to as the X, Y, and Z axes. In addition to these three, the tool can also rotate around two of these axes, allowing it to reach more angles and sides of the material. This is where the “5-axis” term comes from, as it represents the three linear movements plus the two rotational movements. Because of these extra movements, 5-axis CNC machines can create intricate shapes and designs that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional 3-axis machines, which can only move in the X, Y, and Z directions without rotation. This advanced capability allows for faster production, better accuracy, and more complex parts.
In CNC turning, the material (usually a metal or plastic rod) is held and rotated at high speed, while a cutting tool moves to remove the unwanted material, shaping the part. It’s similar to how a potter shapes clay on a spinning wheel. This process is best for creating cylindrical or round parts. On the other hand, CNC milling is like the sculptor using a chisel to shape a block of material. The material stays stationary while the cutting tool moves around and across it, cutting and carving the material into the desired shape. CNC milling can create more complex shapes and is suitable for both flat and curved surfaces.
INQUIRY
CATEGORIES
LATEST NEWS
CONTACT US
Contact: Miss.Gu
Phone: 18090076983
E-mail: kate@khled.com
Whatsapp:8618090076983
Add: Guangdong Province, China TianHe District, GuangZhou Num 899